Global
Submitted by petermeisen on
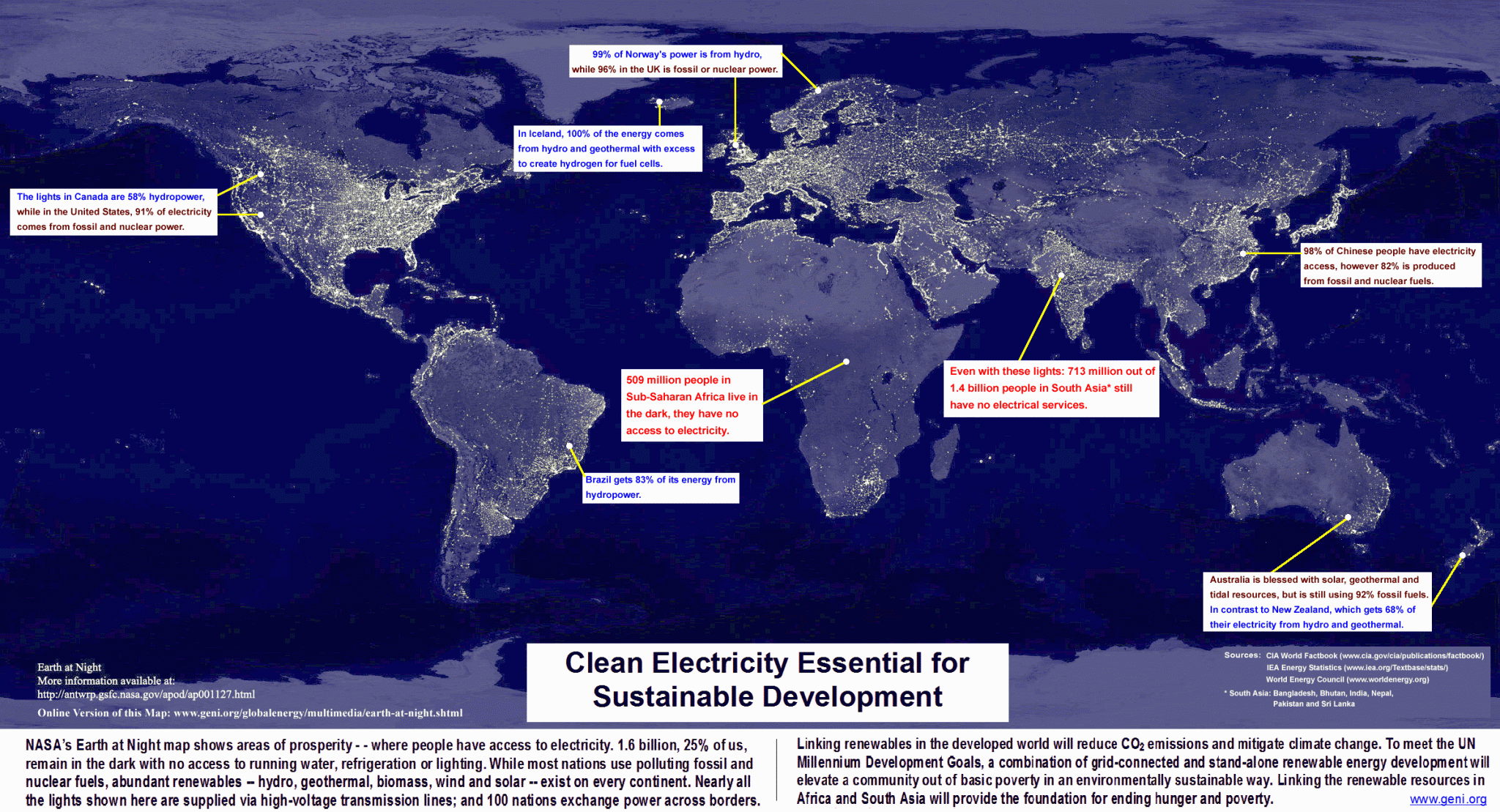
Current Conditions & Driving Factors Helping or Hindering Sustainability
Submitted by Christoph on
Global - Psychological/Social Considerations
Submitted by Christoph on
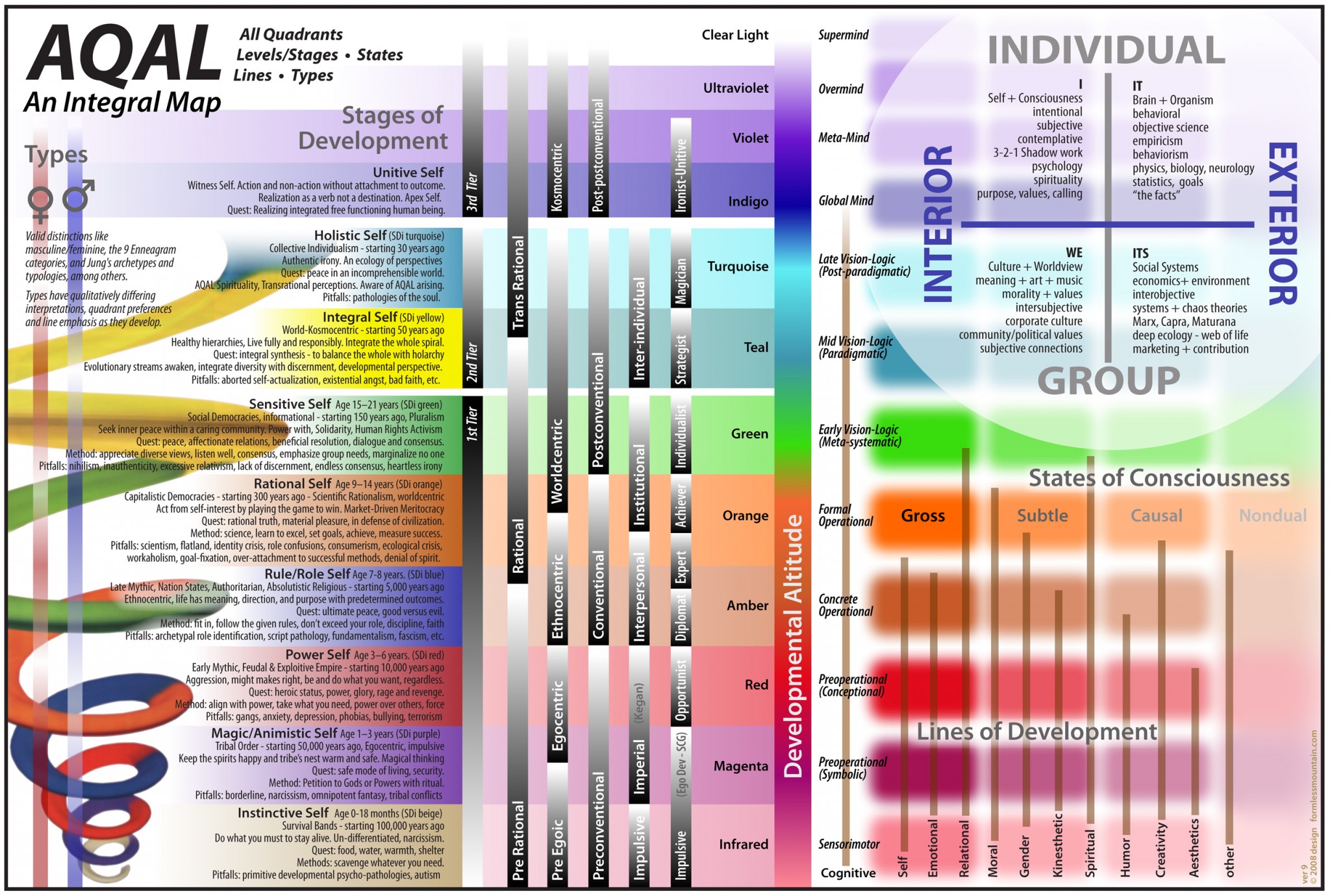
Integral Model of Consciousness - AQAL Map
Submitted by Dan Noble on
Food crisis caused by biofuels?
Submitted by wrscpmd on
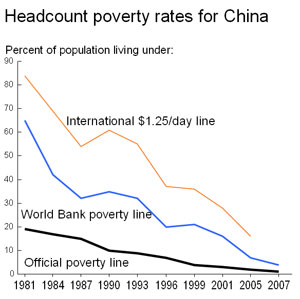
New global poverty estimates confirm China’s leading role in meeting MDGs
Submitted by wrscpmd on
A Global Shift to Renewable Energy
Submitted by wrscpmd on
Megacities
Submitted by wrscpmd on
Glacial Melt And Ocean Warming Drive Sea Level Upward
Submitted by glenshewchuck on
Glacial Melt And Ocean Warming Drive Sea Level Upward
Submitted by glenshewchuck on