Global
Submitted by shermmarshall on
The literacy injustice: 493 million women still can't read
Submitted by shermmarshall on
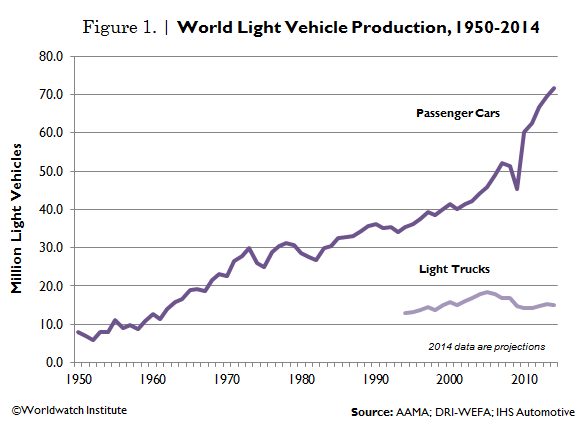
Auto Production Sets New Record, Fleet Surpasses 1 Billion Mark
Submitted by shermmarshall on
Sustainable development goals face $2.5 trillion funding shortfall
Submitted by shermmarshall on
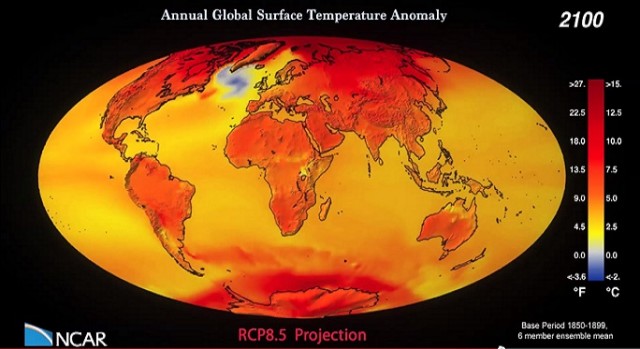
Annual CCSM4 Global Surface Temperature Anomaly, 1850-2100, RCP8.5 Projection
Submitted by patrickpoon7 on
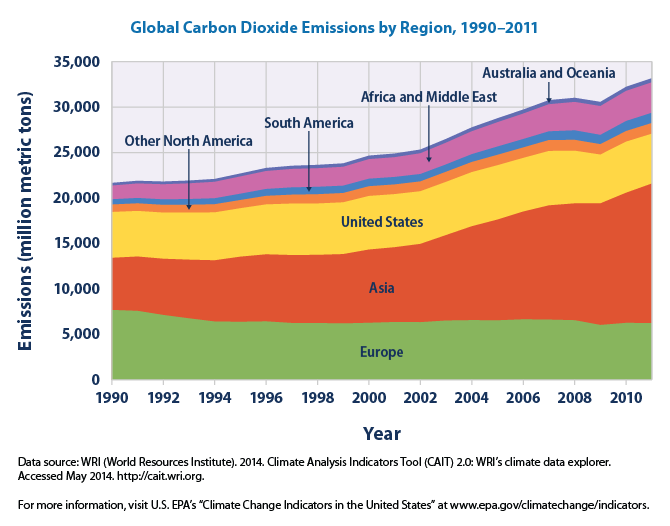
Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions by Region, 1990-2011
Submitted by c.bernhardt.14 on
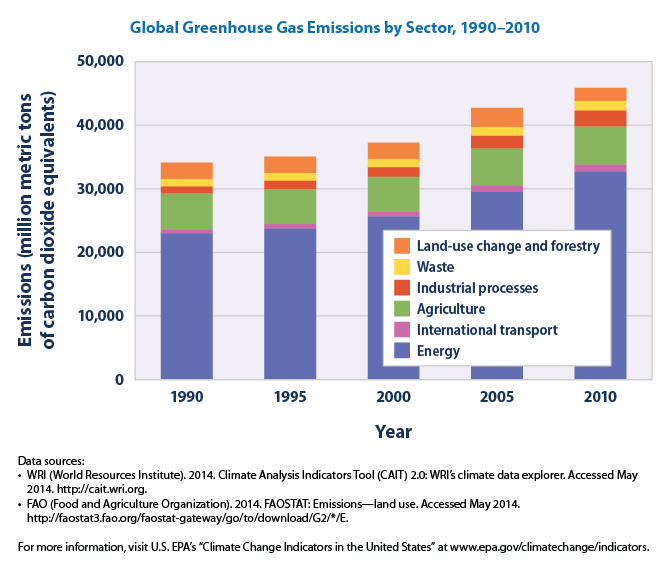
Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Sector, 1990-2010
Submitted by c.bernhardt.14 on
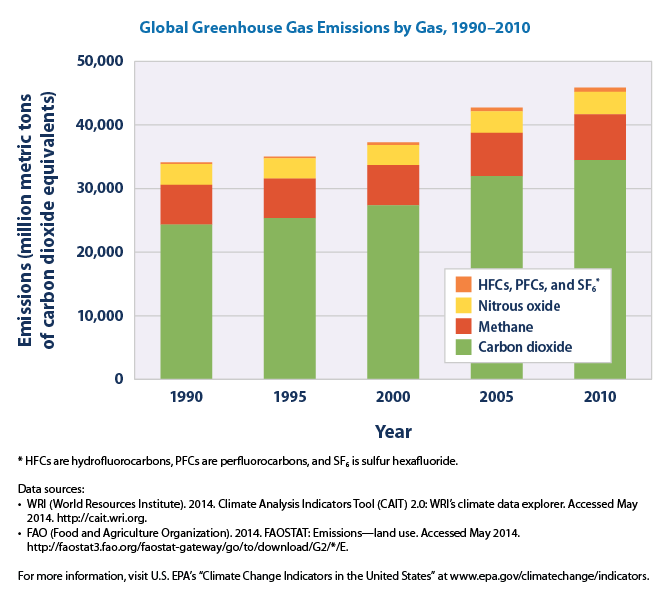
Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Gas, 1990-2010
Submitted by c.bernhardt.14 on
Global Atmospheric Concentrations of Carbon Dioxide Over Time
Submitted by c.bernhardt.14 on
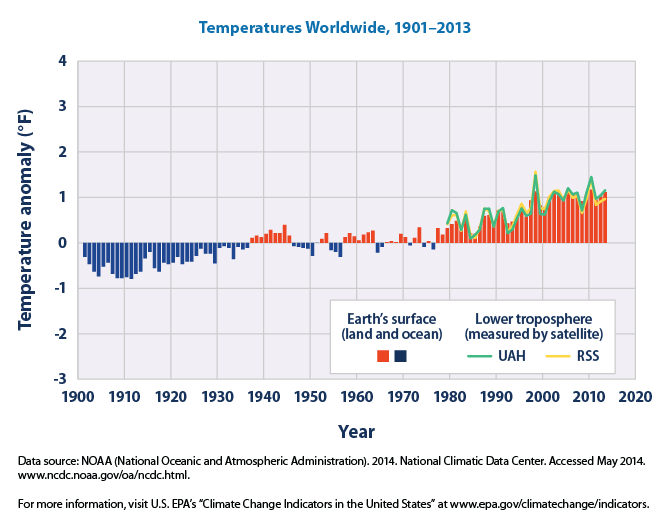
Temperatures Worldwide, 1901-2013
Submitted by c.bernhardt.14 on